Fermetics trial with IntelliBond M and Optimin Mn
Dairy nutritionists are often concerned about the under-supply of trace minerals. Both the level of supplementation and the source of trace minerals used in dairy cattle diets can significantly impact NDF digestibility. The source of trace minerals fed can have a negative impact on rumen fermentation and feed efficiency, which in turn can impact the lactational performance, health and fertility of dairy cattle.
According to Oba and Allen, if NDF digestibility increases by 1 point, dry matter intake might increase by 0.17 kg and milk production by 0.25 kg of 4% fat-corrected milk. A meta-analysis showed that feeding hydroxy trace minerals instead of sulphates improves NDF digestibility by 1.7% points.
Limited data are available on the effects of supplemental mineral sources on rumen fermentation of dairy cattle. The Fermentics model was used to test the effect of different manganese sources on apparent organic matter disappearance (aOMD) and apparent microbial biomass production (aMBP). Both aMBP and aOMD are correlated with milk production.
Impact of manganese source on rumen fermentation, material and methods
Manganese trace minerals were added to containers containing a mix of 80% buffer and 20% cattle rumen fluid and bags containing TMR for cattle. The containers were incubated for 48-h in a 39.5°C water bath. Data were analysed using PROC MIXED (SAS Institute Inc, Cary, NC). A p-value ≤ 0.05 was considered significant. The different manganese sources included in the trial were IntelliBond M, Optimin Mn, Zn oxide and Zn sulphate. The manganese trace minerals were compared to a control with no trace mineral source included.
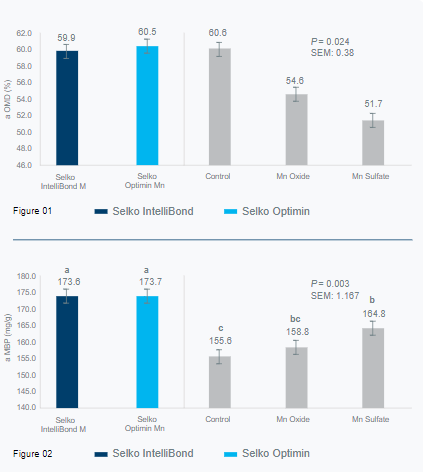
Figure 1: Apparent Organic Matter Disappearance of Selko IntelliBond M and Selko Optimin Mn vs other manganese trace mineral products for dairy cattle.
Figure 2: Apparent Microbial Biomass Production of Selko IntelliBond M and Selko Optimin Mn vs other manganese trace mineral products for dairy cattle.
Impact of manganese source on rumen fermentation, results
Mn oxide and Mn sulphate reduced aOMD relative to the control (P<0.001), whereas IntelliBond M and Optimin Mn were similar to the control (see Figure 1).
IntelliBond M and Optimin Mn had higher apparent microbial biomass production (aMBP) than the control, Mn sulphate and Mn oxide treatments (P<0.01, see Figure 2).
Conclusion
Compared to the control without a manganese source, apparent Microbial Biomass Production (aMBP) was increased by IntelliBond M and Optimin Mn, suggesting a positive impact of manganese supplementation on rumen fermentation of dairy cattle. Compared to the control, IntelliBond M and Optimin Mn did however not increase apparent Organic matter Disappearance (aOMD). Compared to Mn sulphate and Mn oxide, both for Optimin Mn and IntelliBond M, aMBP and aOMD were increased, suggesting that the source of manganese supplementation for dairy cattle can have a significant impact on rumen fermentation.
